
Time-domain OCT (TD-OCT): The reference mirror is moving hence enabling coherence gating at different depths in the sample arm.There are different practical realizations of OCT: Image depths of several mm into the tissue can be achieved. In this way, cross-sectional imaging can be realized – much like ultrasound – but with a much higher resolution. The sensitivity of OCT is so high it can detect even the weak signals from sub-surface reflections. This coherence gating lets the detection system to discriminate between reflections from closely spaced reflectors enabling high-resolution imaging.
The two light beams will interfere if the difference in the path lengths is within the coherence length of the optical signal. The light from both arms originates from the same light source. Light from one arm is reflected or scattered off the subject under investigation and interferes with light from a reference arm. The number of OCT applications using SuperK sources is increasing rapidly. The SuperK supercontinuum lasers offer several key parameters relevant for UHR-OCT: An increasing amount of research is made in OCT outside the ophthalmology field. OCT applications are, however, not limited to ophthalmology. Over the last 20 years, OCT has become an essential imaging tool in ophthalmology with particular emphasis on detailed analysis of the retina and the surrounding tissue. A very thorough description of principles and applications has been provided by Professor Drexler from the Medical University Vienna and Professor Fujimoto from MIT in “Optical Coherence Tomography: Technology and Applications”. The OCT principle for imaging was first demonstrated in 1991 by Professor Huang et al.

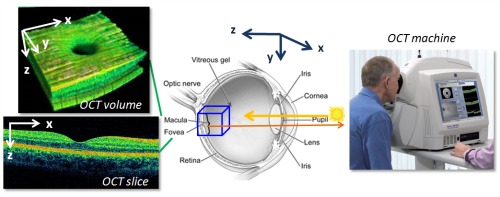
This is a huge advantage compared to alternative microscopy techniques where you can only investigate the surface or shallow layers of the subject.Ĭross-sectional or 3D imaging is relevant for various applications, ranging from the analysis of tissue in medical applications to visualization of sub-micron structures in manufacturing. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) enables cross-sectional or 3D imaging of the subject under investigation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
